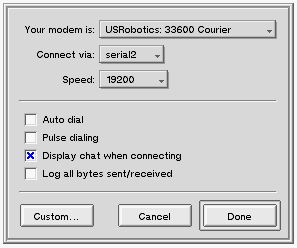
When you install your modem, you configure it through the modem configuration panel that's presented by the Dial Up Networking (DUN) preferences application (as shown below).

DUN asks you to identify your modem by selecting from the list of modem vendors and model numbers displayed in the Your modem is: list. Your vendor/model choice generates a default initialization string (the modem's init string) that's sent to the modem when you dial out. The default init string should be sufficient for most modem uses, but there are times when you may want to add to the string, or modify it in some way.
To edit the init string, click the Custom button in the modem configuration panel. If this is a new configuration, you'll see a panel that asks you to name your modem init string.
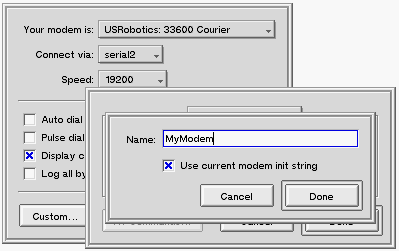
If you want to modify the default init string (this is the recommended approach), check the Use current modem init string checkbox. If you want to configure the string from scratch, leave the box unchecked. After you click Done, you'll see the init string panel itself.
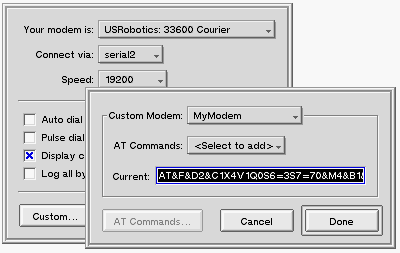
The Current: text field displays the current init string. (If you're rolling your own, the init string will be, simply, "AT"). This is the string you want to modify. After the initial "AT" (which appears at the head of all init strings), each of the elements in the string is an AT command that sets a particular aspect of the modem. You can edit this string to add, remove, or modify the AT commands it contains. The AT commands are listed in the following section.
| %Cn | Data compression control. |
| %En | Line quality monitor. |
| &Cn | DCD carrier detect control. |
| &Dn | Ignore (0) or use (1) DTR option. |
| &Fn | Restore factory default 0 or 1. |
| &Gn | Guard tone control. |
| &Kn | Data flow control. |
| &Qn | Communication (sync/async) method. |
| &Rn | IRTS/CTS (hardware) flow control. |
| &Tn | Test request controls. |
| &V | View current configuration. |
| &Wn | Store user profiles. |
| &Yn | Restore default user profiles. |
| &Zn=x | Store dial string x in location n (0-3). |
| +++ | Escape sequence. Does not use AT prefix. |
| :En | Enable (1) or disable (0) compromise equalizer. |
| ? | Read currently selected S register. |
| \An | Select maximum MNP block size. |
| \Bn | Transmit break n x 100 ms. |
| A | Pick up line and attempt to answer call |
| A/ | Redo last command. Does not use AT prefix. |
| Bn | CCITT or Bell selection |
| Dn | Dial number n. For example: ATD 5551212 [enter] |
| En | Enable (1) or disable (0) command echo. |
| Hn | Go off (1) or on (0) hook. |
| In | Product identification. |
| Ln | Speaker volume control. For example:
|
| Mn | Speaker control. For example:
|
| Nn | Enable (1) or disable (0) automode detection. |
| On | Command mode control. |
| P | Use pulse dialing. |
| T | Use tone (DMTF) dialing. |
| Qn | Enable (0) or disable (1) result codes. |
| Sn | Return the value of S register n. |
| Sn=x | Write x into S register n. |
| Sn? | Read S register n. |
| Vn | Report numeric (0) or verbose (1) result codes. |
| Wn | Report DTE n speeds (n=0,1,2) |
| Xn | Extended result code control. |
| Yn | Enable (1) or disable (0) long space disconnect. |
| Zn | Modem reset. |